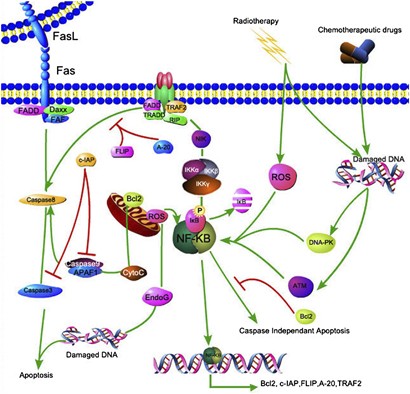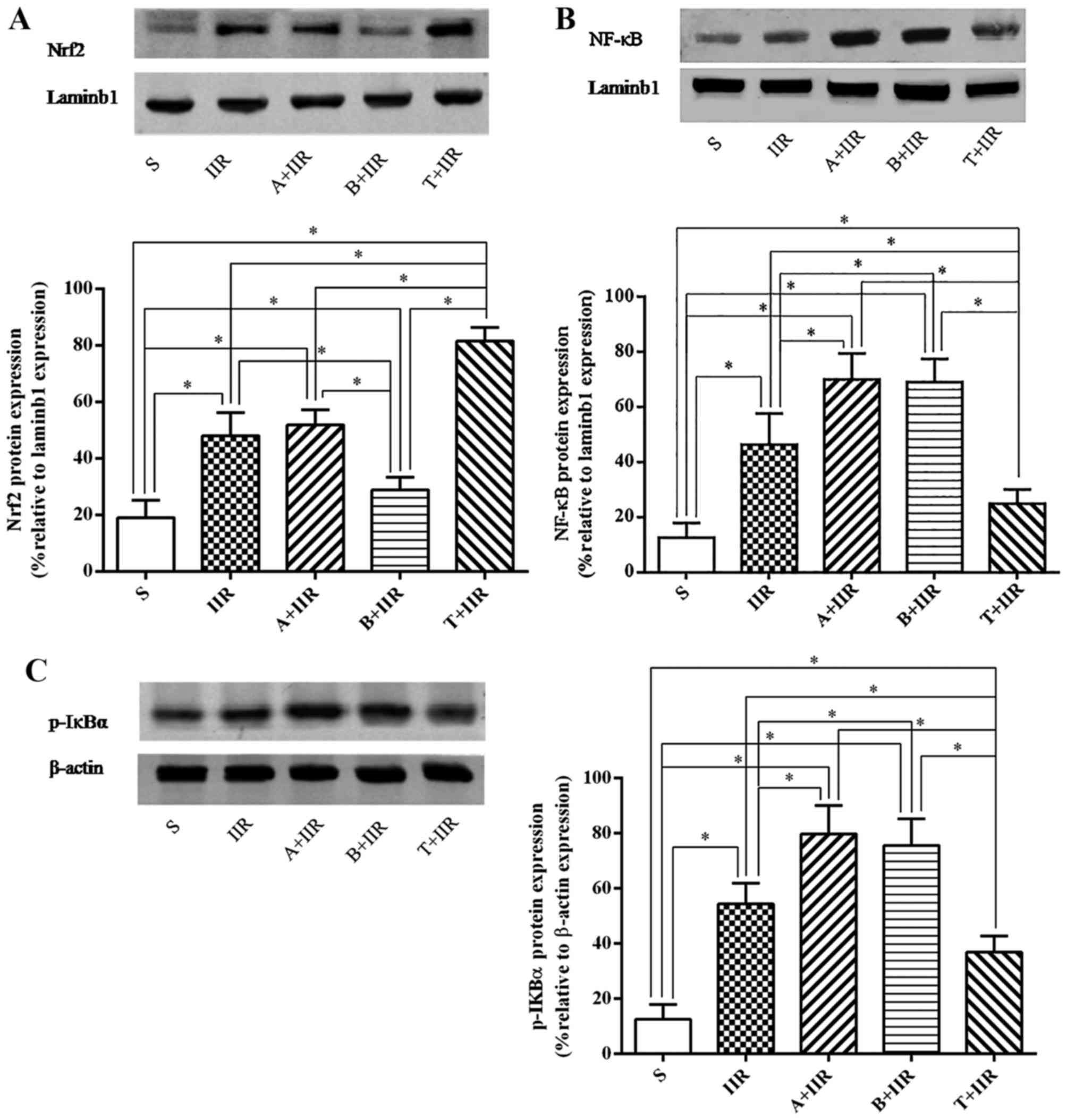
Transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB contribute to inflammation and apoptosis induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in mice
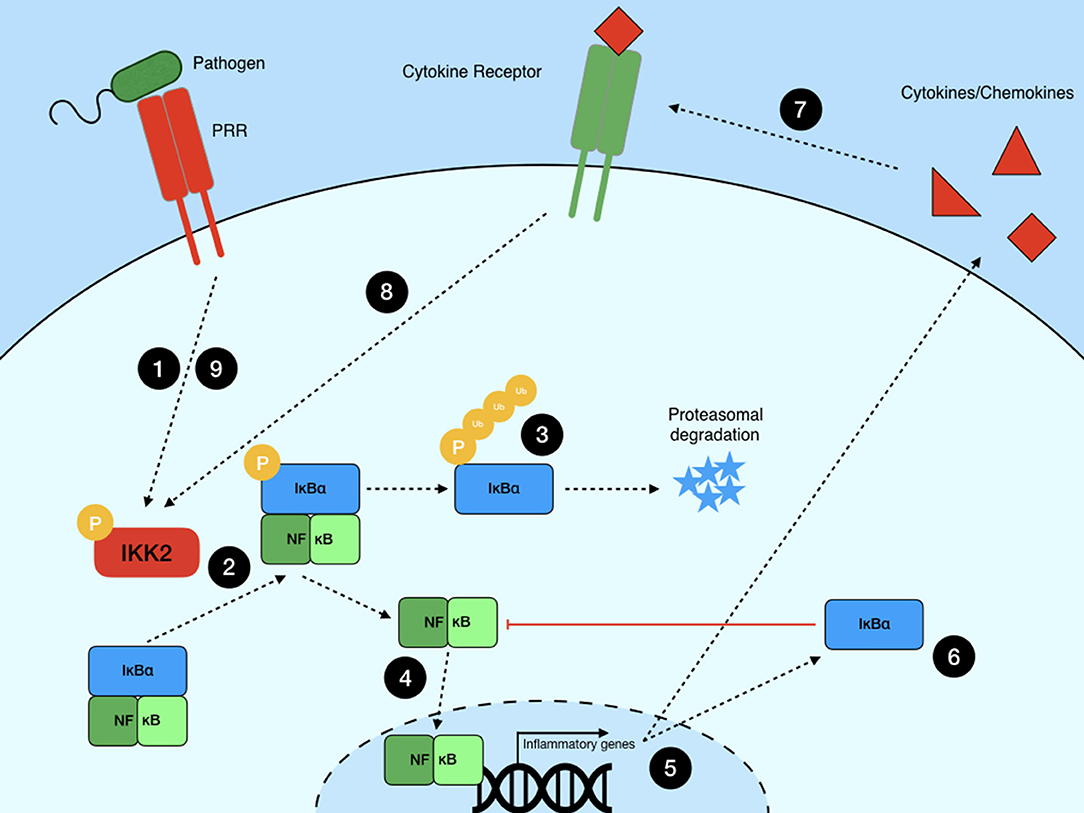
Frontiers | NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages: Dynamics, Crosstalk, and Signal Integration | Immunology
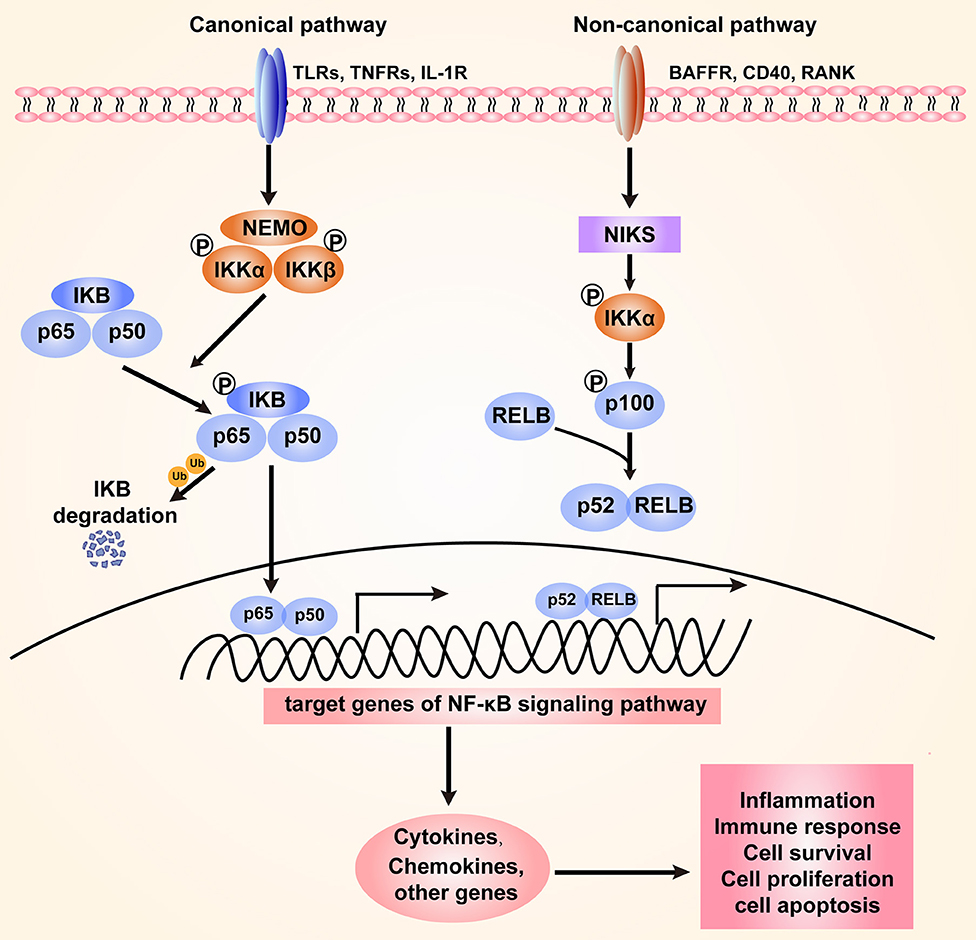
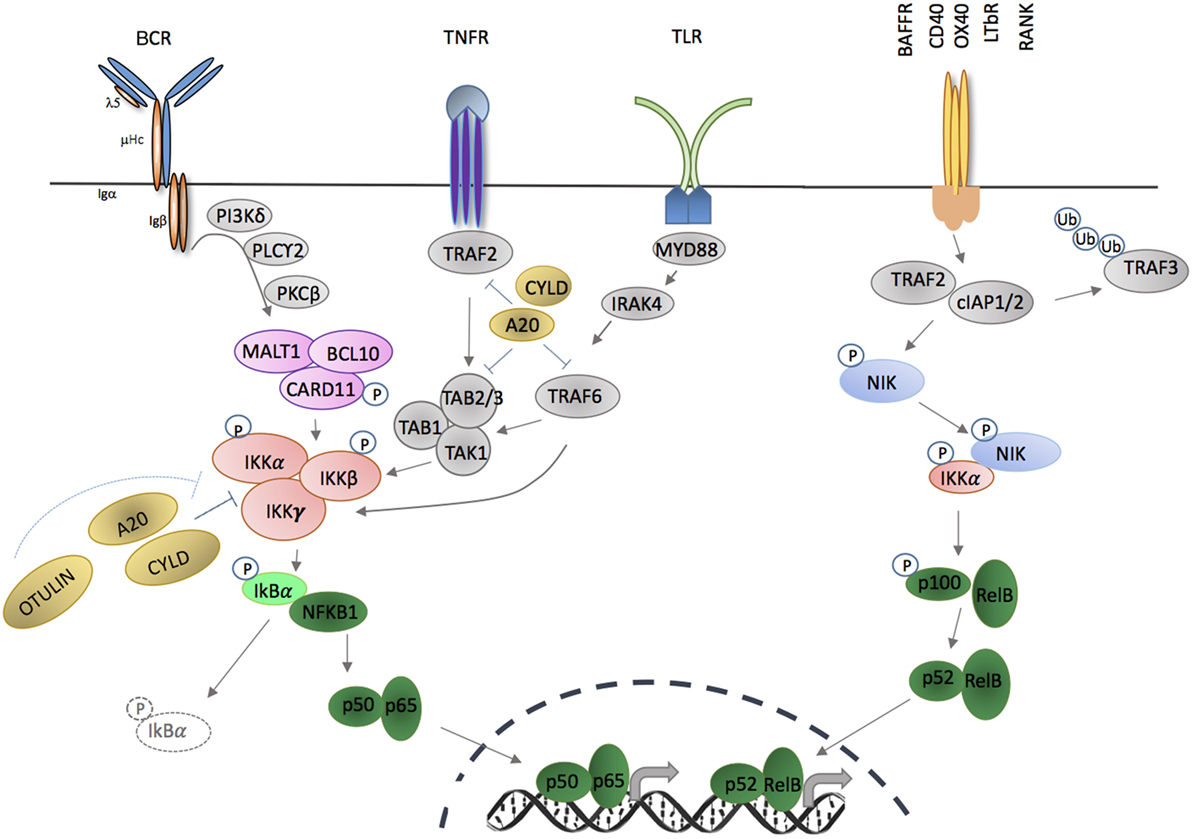
Frontiers | The NF-κB Signaling Pathway, the Microbiota, and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis: Recent Advances | Immunology
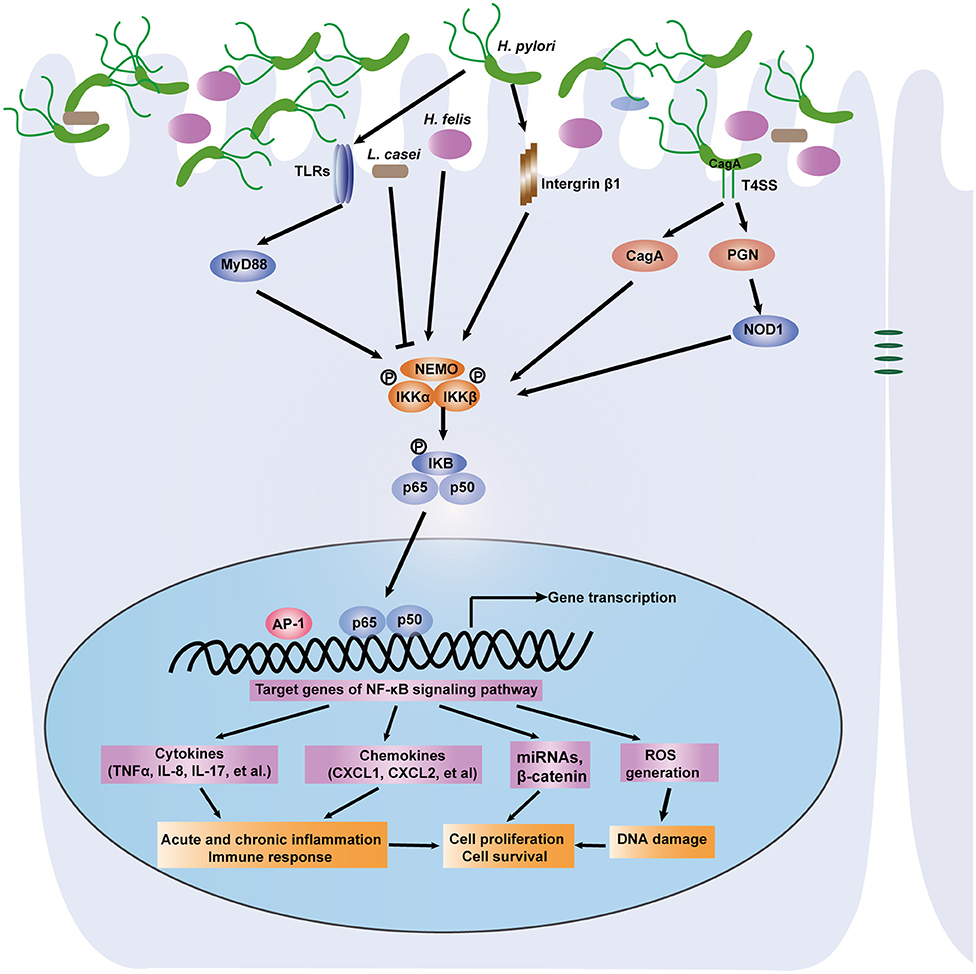
Frontiers | The NF-κB Signaling Pathway, the Microbiota, and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis: Recent Advances | Immunology

Caudal acts as a gut-specific repressor for NF-kB-dependent AMP genes.... | Download Scientific Diagram
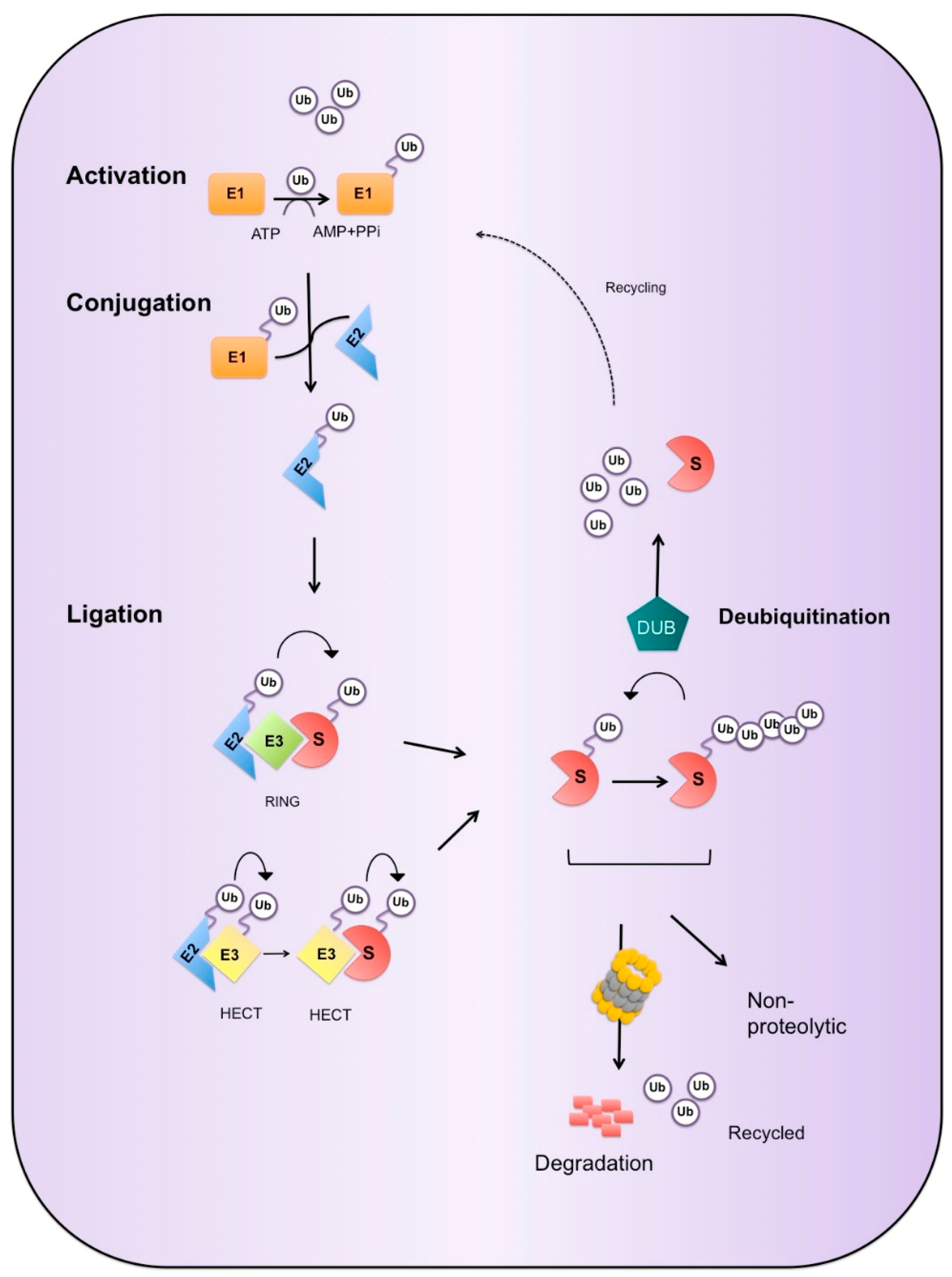
Cells | Free Full-Text | The Ubiquitination of NF-κB Subunits in the Control of Transcription | HTML
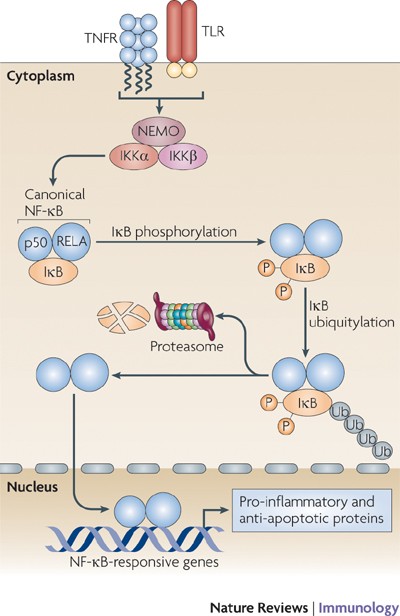
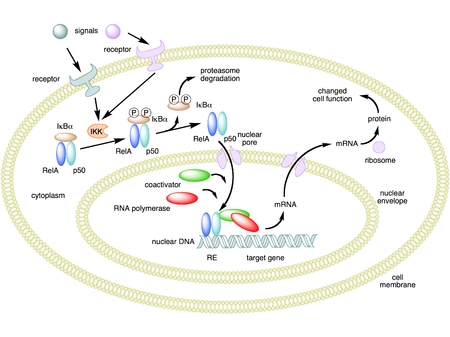
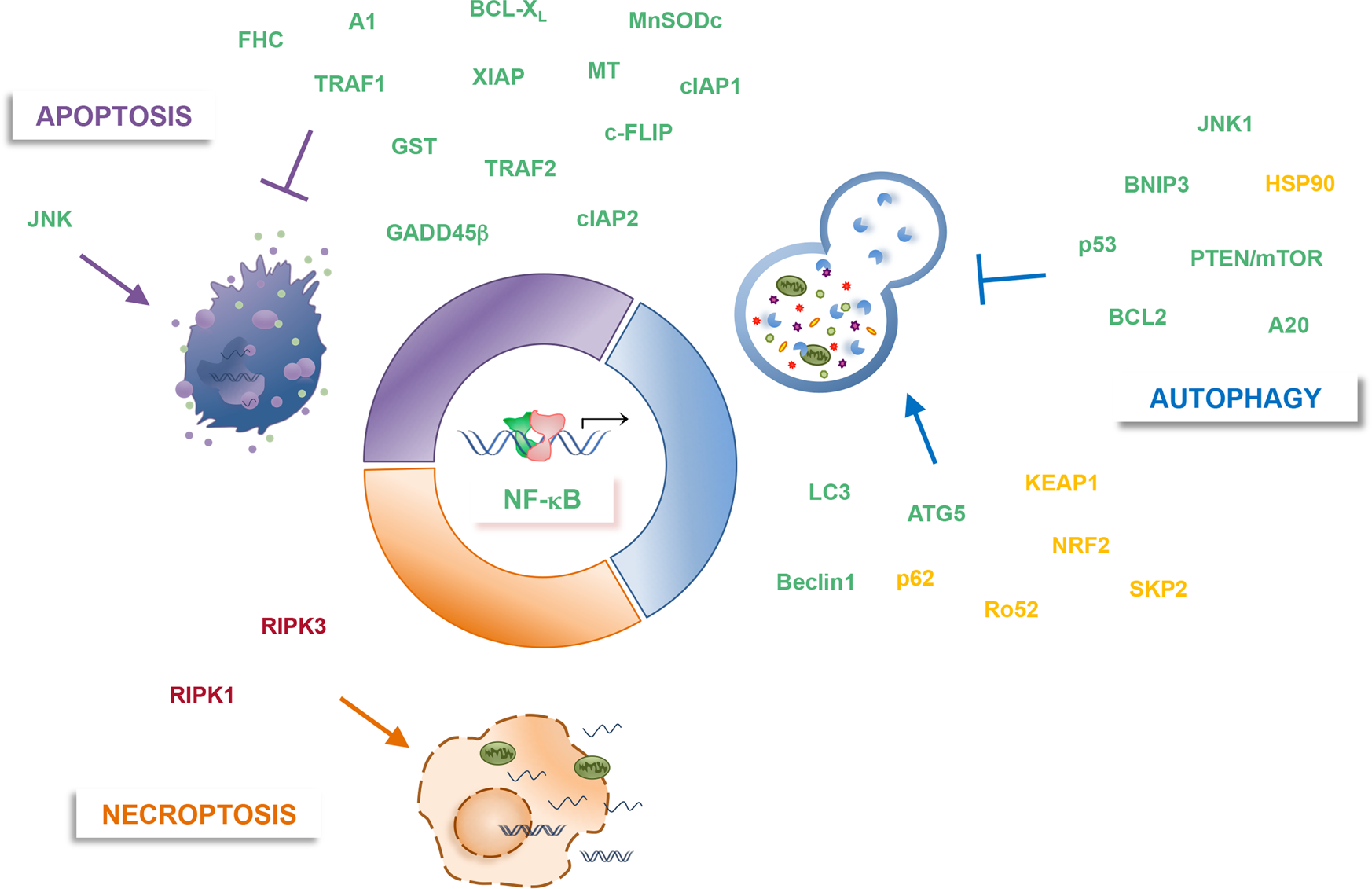
Regulation of tissue homeostasis by NF-κB signalling: implications for inflammatory diseases | Nature Reviews Immunology
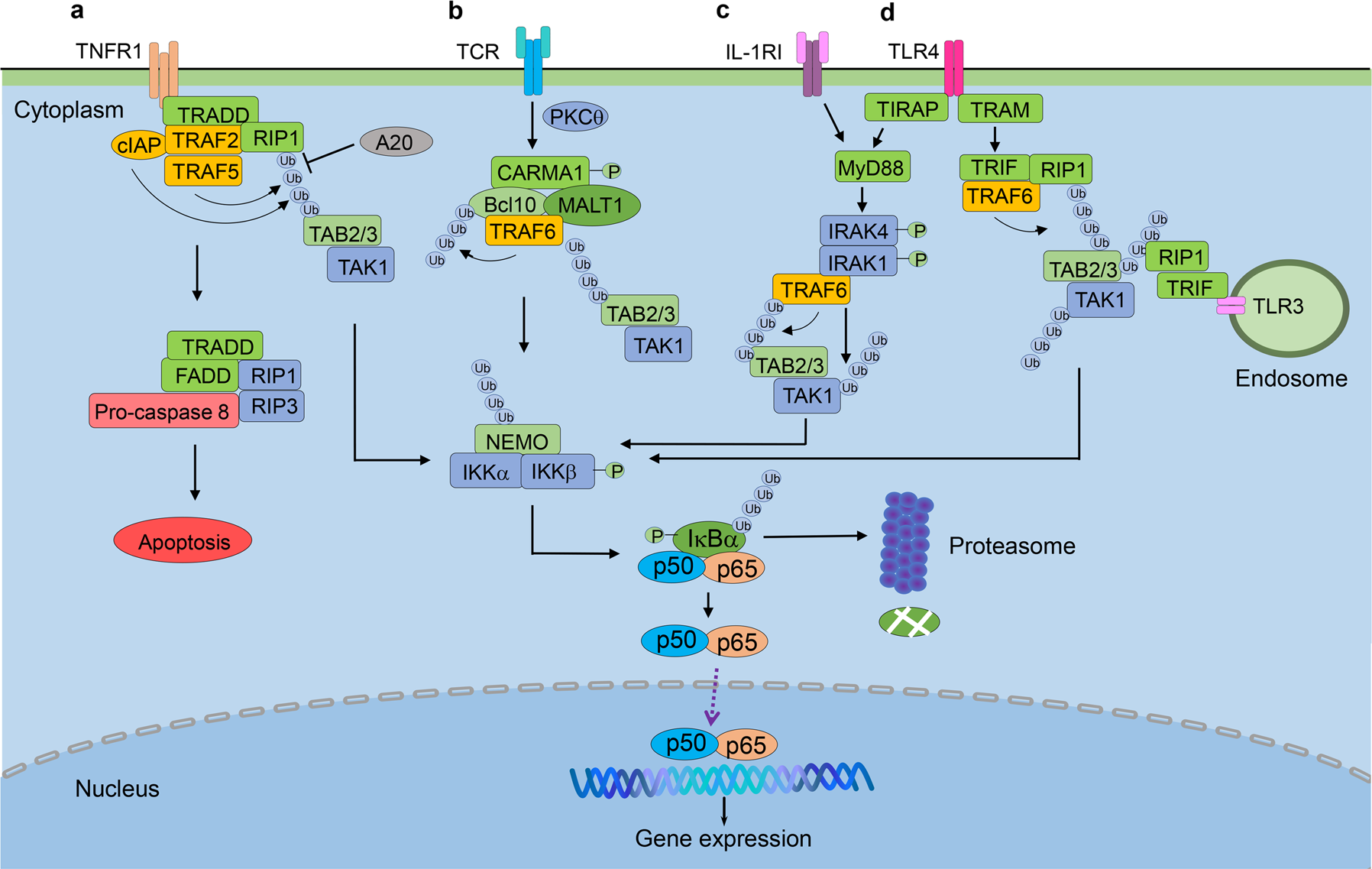
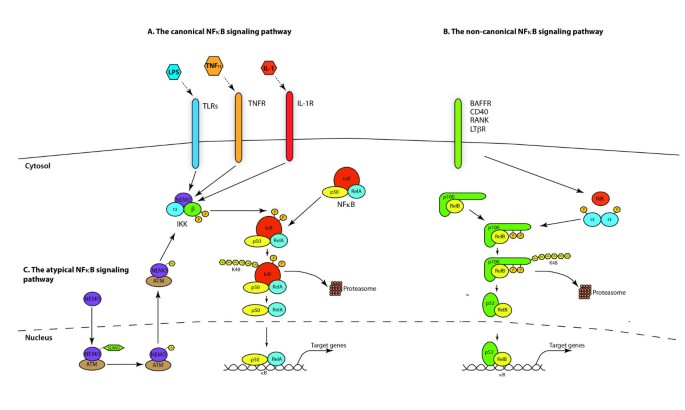
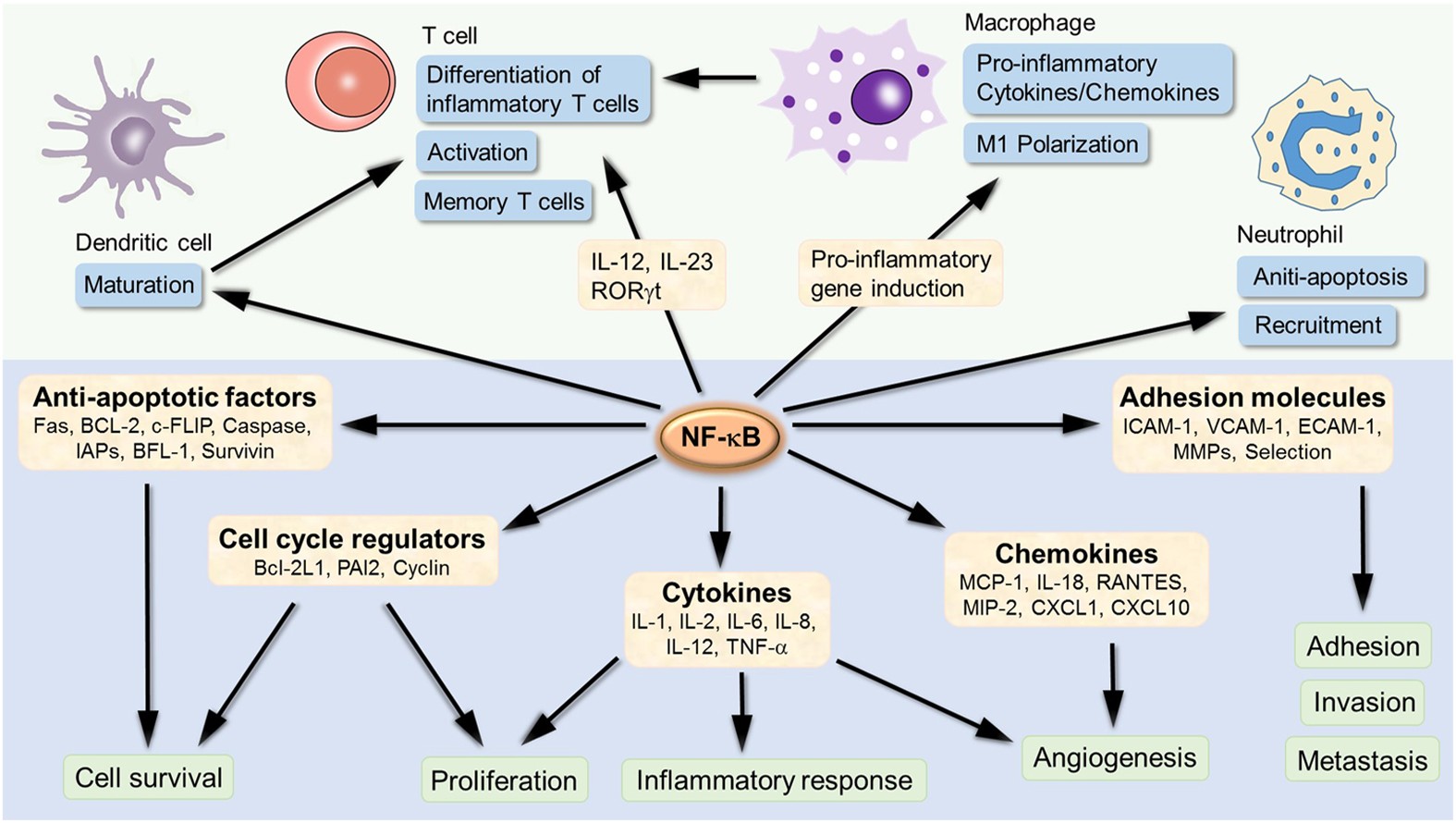
Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy

A Failure of Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Negative Regulation Maintains Sustained NF-κB Activation in Gut Inflammation* - Journal of Biological Chemistry
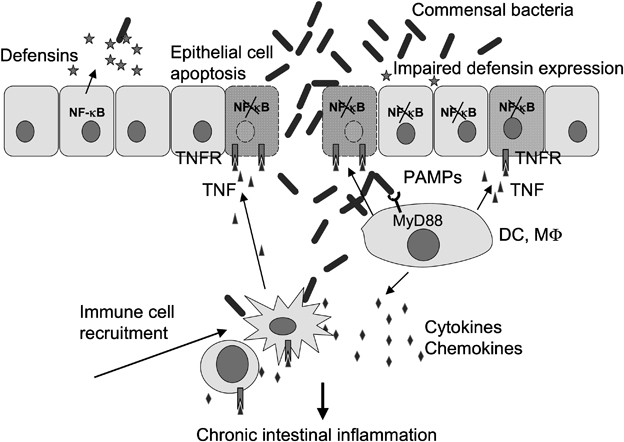
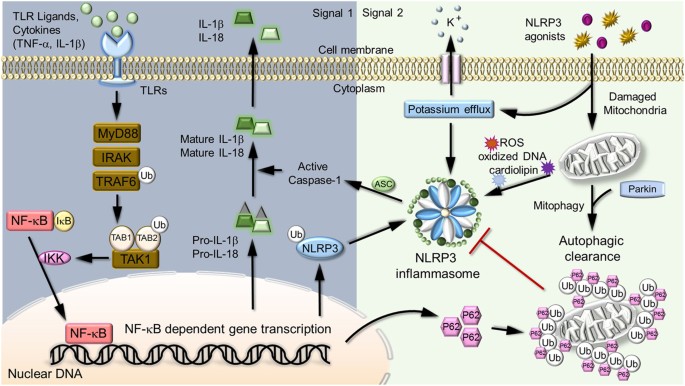
IKK/NF-κB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells controls immune homeostasis in the gut | Mucosal Immunology

An epithelial Nfkb2 pathway exacerbates intestinal inflammation by supplementing latent RelA dimers to the canonical NF-κB module | PNAS
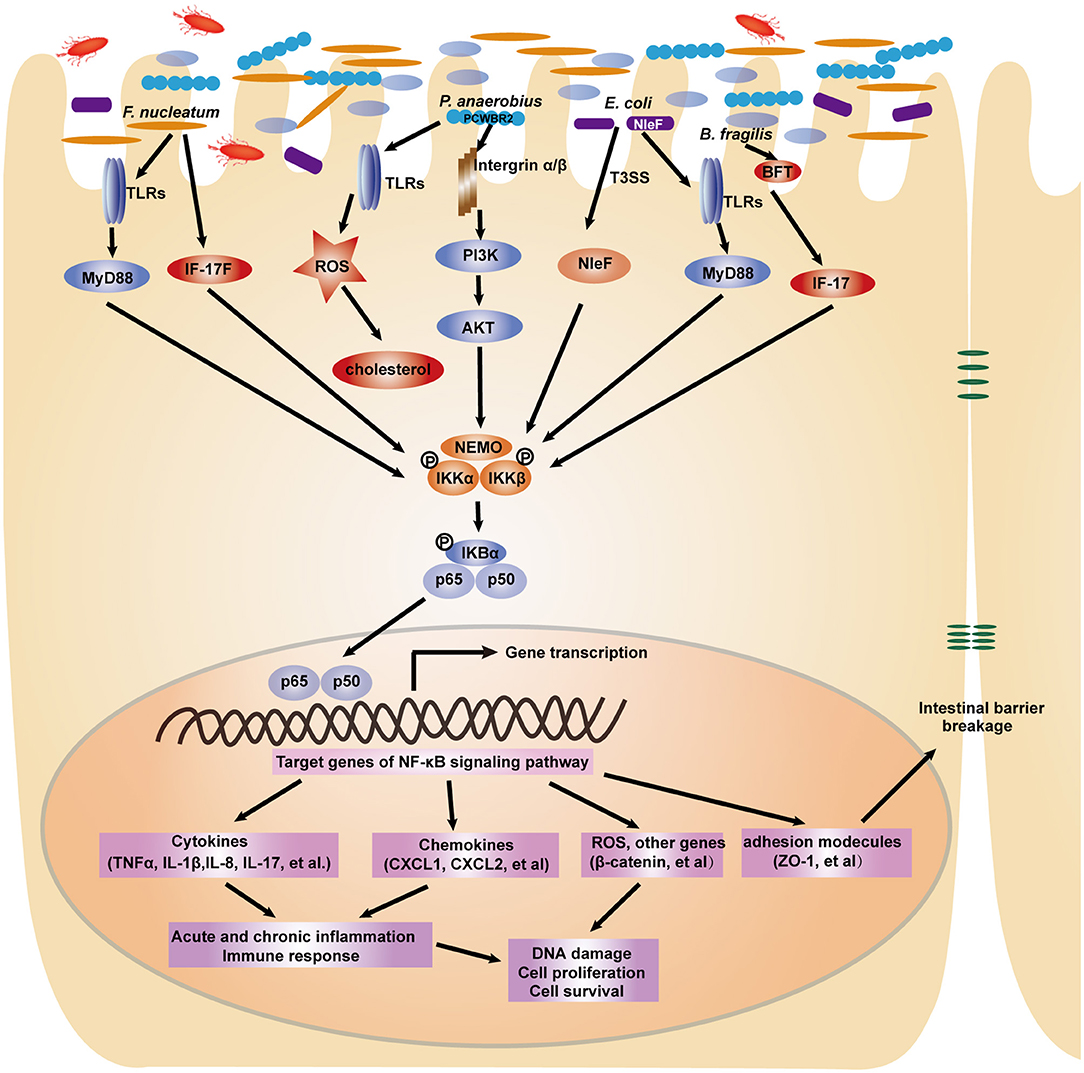
Frontiers | The NF-κB Signaling Pathway, the Microbiota, and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis: Recent Advances | Immunology
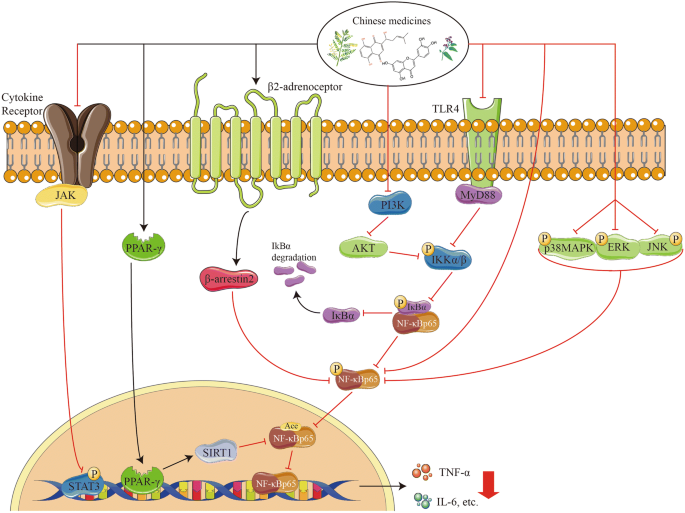
Targeting NF-κB pathway for treating ulcerative colitis: comprehensive regulatory characteristics of Chinese medicines | Chinese Medicine | Full Text