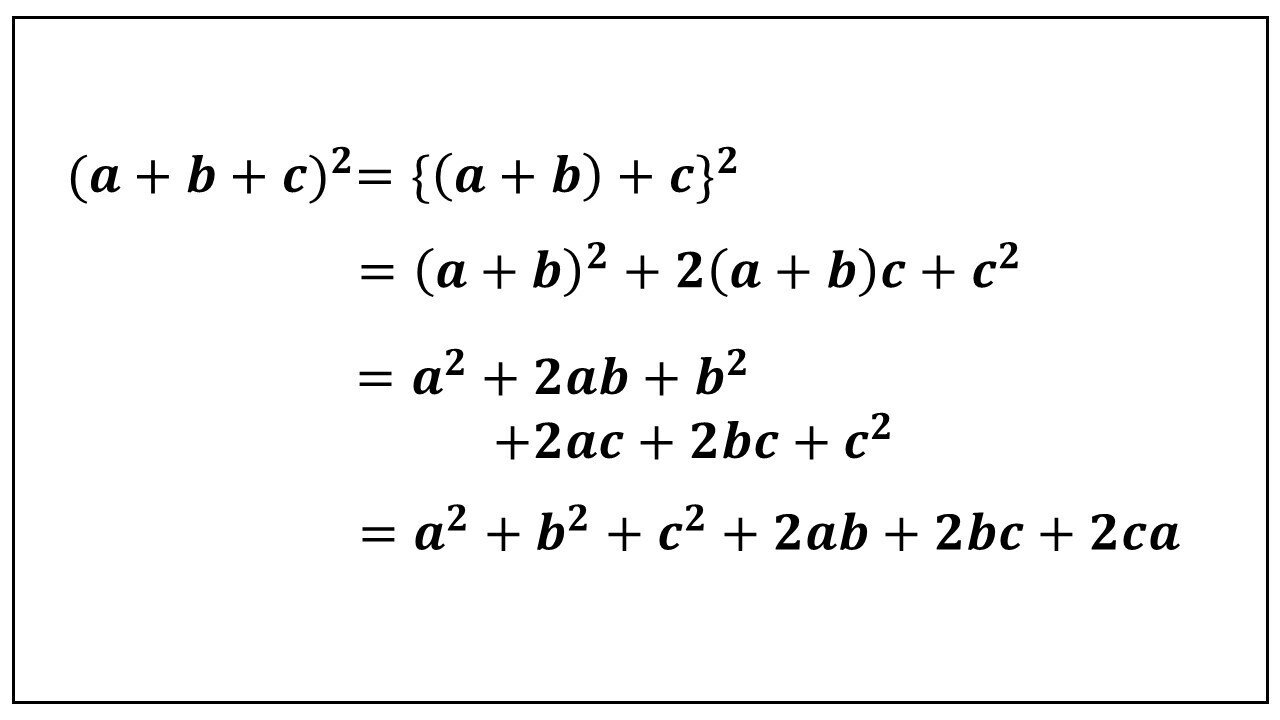Cho b^2=ac CMR : (a+2019b)^2/(b+2019c)^2=a/c - Toán học Lớp 7 - Bài tập Toán học Lớp 7 - Giải bài tập Toán học Lớp 7 | Lazi.vn - Cộng đồng Tri thức

Warm-up 1. Solve the following quadratic equation by Completing the Square: x x + 15 = 0 2. Convert the following quadratic equation to vertex format. - ppt download
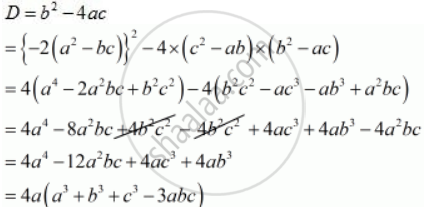
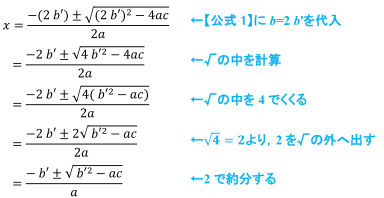
If the Roots of the Equation (C2 – Ab) X2 – 2 (A2 – Bc) X + B2 – Ac = 0 in X Are Equal, Then Show that Either a = 0 Or A3 + B3 + C3 = 3abc - Mathematics | Shaalaa.com
ad ≠ bc, then prove that the equation (a^2 + b^2)x^2 + 2(ac + bd)x + (c^2 + d^2) = 0 has no real roots. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

if sin alpha and cos alpha are the roots of the equation ax 2 bx c 0then prove that a 2 2ac b 2 - Mathematics - TopperLearning.com | eq166100
Using quadratic formula, solve the following equation for x: abx^2+(b^2-ac)x-bc=0 - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

Using the quadratic formula, solve following equation for x: abx2 + (b2 - ac)x - bc = - Maths - Quadratic Equations - 1009445 | Meritnation.com